Vaccination Model
Now, we are going to write a model for Vaccination. This Vaccination model will store informations like patient, campaign, slot, vaccination status and such informations.
Look at the class diagram of our project and you can find the Vaccination class.
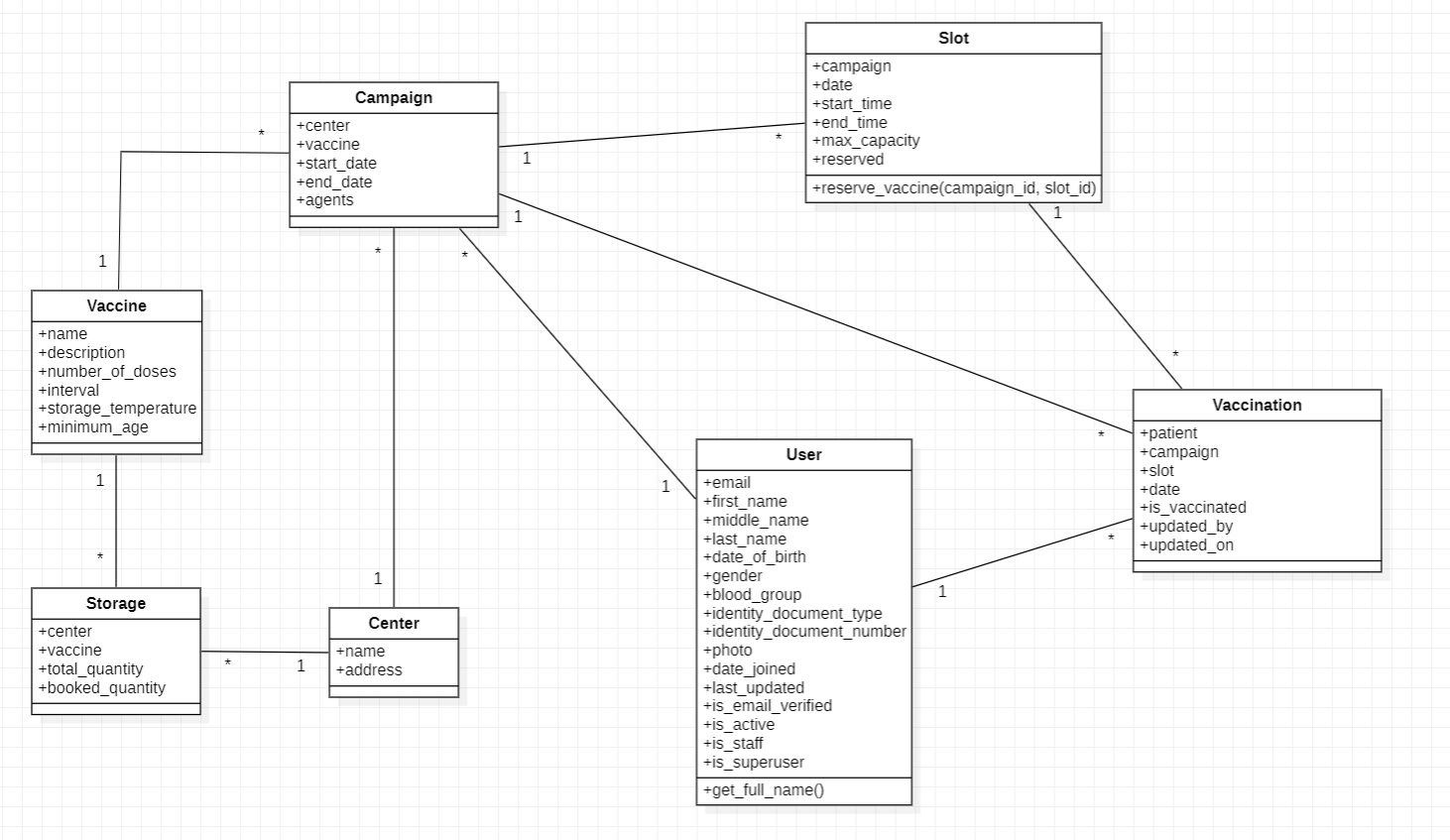
If you study the Vaccination class properly, then you can find that Vaccination class forms many-to-one relationship between User, Campaign and Slot.
Now, let us implement this Vaccination class in django.
Open models.py file of vaccination app.
First we need to import User model, Campaign model and Slot model.
from django.contrib.auth import get_user_model
from campaign.models import Campaign, Slot
User = get_user_model()
Now create a Vaccination model.
class Vaccination(models.Model):
First let us start with User model. We will add patient field that maps many-to-one relationship between vaccination and user model.
patient = models.ForeignKey(User, related_name="patient", on_delete=models.CASCADE)
We have used related_name model field option in this database field. We use related name to specify the name of reverse relation from the User model back to this model. We will learn more about it later on, in this course.
Now, let us add another field named campaign that maps many-to-one relationship between vaccination and campaign model.
campaign = models.ForeignKey(Campaign, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
After that, add another field named slot that maps many-to-one relationship between vaccination and slot model.
slot = models.ForeignKey(Slot, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
After that, add another field named "date" that stores the date when the vaccination of user is approved.
date = models.DateField(null=True, blank=True)
After that, we need a field that stores the vaccination status of the pateint.
is_vaccinated = models.BooleanField(default=False)
Now, we will add another field named updated_by that maps many-to-one relationship between vaccination and user model. It stores the user who updates the vaccination object.
updated_by = models.ForeignKey(User, null=True, blank=True, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
Finally, we need to add a field named updated_on. Each time when the vaccination object gets updated, it will store the date and time of the updation activity.
updated_on = models.DateTimeField(auto_now=True, null=True)
We have added auto_now = True as a model field option. It basically updates the field with the current date and time when update takes place.
Finally, add the str method to represent each Vaccination object in human readable form.
def __str__(self):
return self.patient.get_full_name() + " | " + str(self.campaign.vaccine.name)
Now, register the vaccination model in the admin panel.
from vaccination.models import Vaccination
admin.site.register(Vaccination)
Create the migration file.
python manage.py makemigrations
Migrate the changes to the database
python manage.py migrate
Start the development server and perform CRUD operations on Vaccination model.
At last, push the changes to remote repository
git add .
git commit -m "Added Models and Migrations"
git push origin main